How Oxygen Generators Improve Hospital Oxygen Supply

Hospitals often struggle to maintain a steady oxygen supply, especially during emergencies or peak demand. You can address this challenge by adopting an oxygen generator, a solution that ensures a continuous flow of oxygen directly on-site. These systems, particularly the Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) type, offer long-term cost savings. While the initial investment may seem high, they eliminate reliance on external suppliers and protect against fluctuating oxygen prices. This stability allows hospitals to plan budgets more effectively. Additionally, integrating renewable energy sources can make these systems even more sustainable, reducing their environmental impact.
Key Takeaways
-
Oxygen generators give a steady supply of oxygen for patients.
-
Making oxygen onsite can save hospitals up to 90% in costs.
-
Onsite systems lower the need for outside suppliers and improve efficiency.
-
They help the environment by cutting transport and carbon pollution.
-
Using oxygen generators supports global green goals and helps patients.
What Are Oxygen Generators and Their Role in Healthcare?
Definition and Functionality of Oxygen Generators
An oxygen generator is a device that produces oxygen from the surrounding air. It uses advanced technology, such as pressure swing adsorption (PSA), to separate oxygen from nitrogen and other gases. This process ensures a steady supply of high-purity oxygen, which is essential for medical use. The system typically includes components like an air compressor, air dryer, and oxygen purification processor to maintain efficiency and reliability.
| Key Operational Statistic | Description |
|---|---|
| Methods of Separation | Pressure swing adsorption (PSA), membrane separation, cryogenic distillation |
| Concentration Levels | Ranges from 90% to over 99.9% purity |
| Power Source | Powered by electricity or other energy sources |
| Portability | Large, stationary units for industrial or medical use |
| Typical Uses | Steelmaking, chemical processing, water treatment, aerospace |
Oxygen generators are designed to meet the demands of healthcare facilities, ensuring that medical-grade oxygen concentration is always available. This makes them a critical part of modern hospital infrastructure.
Importance of Oxygen in Medical Settings
Oxygen plays a vital role in saving lives. It is listed as an essential medicine by the World Health Organization (WHO) and is used in various treatments. Oxygen therapy reduces death rates in patients with severe pneumonia and other respiratory illnesses. It is also crucial during surgeries and trauma care.
-
Medical oxygen is essential for treating respiratory conditions like COPD, pneumonia, and COVID-19.
-
Hospitals rely on oxygen therapy to improve patient outcomes and reduce mortality rates.
-
WHO guidelines emphasize the importance of maintaining high-purity oxygen for medical use.
By ensuring a continuous supply of medical oxygen, hospitals can provide better care for patients facing critical health challenges.
How Oxygen Generators Fit Into Hospital Infrastructure
Oxygen generators integrate seamlessly into hospital systems, acting as a central oxygen generation system. These systems connect directly to the hospital's pipeline, delivering oxygen to various departments. Onsite oxygen generation eliminates the need for frequent cylinder deliveries, reducing logistical challenges.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) systems |
| Capacity | Ranges from 2 to 189 Nm³/h |
| Purity | Up to 95% oxygen purity |
| Energy Consumption | As low as 1.0 kW/m³ of oxygen |
| CO2 Emissions | Low CO2 emissions |
| Certifications | ISO 9001, ISO 13485, ISO 14001, among others |
Hospitals benefit from onsite oxygen generation by reducing dependency on external suppliers. This central oxygen generation system ensures uninterrupted oxygen availability, even during emergencies. However, proper planning and reliable energy sources are essential for smooth integration.
Challenges of Traditional Oxygen Supply Methods
Dependence on External Suppliers
Hospitals relying on traditional oxygen supply methods often depend heavily on external suppliers. This dependency creates vulnerabilities, especially during emergencies or periods of high demand. The medical oxygen ecosystem involves multiple stages, including production, transportation, and delivery. Each stage increases reliance on external sources.
-
Transportation and distribution are significant cost drivers in traditional oxygen systems.
-
Long distances between production plants and hospitals raise expenses.
-
Optimizing the supply chain is essential to reduce costs and ensure timely delivery.
We used to buy from Addis Ababa so the cost was expensive. But now the cost of oxygen is reduced by 50%. So, the community is getting the treatment in the nearby hospital, meaning financial losses are reduced. —Chief executive officer
Reducing dependency on external suppliers can help hospitals lower costs and improve operational efficiency. Onsite oxygen generation offers a practical solution to this challenge.
High Costs of Bulk Oxygen Delivery
Bulk oxygen delivery is another challenge for hospitals. The costs associated with transporting and storing oxygen cylinders can be substantial. For example:
-
Delivered oxygen can cost up to $5,200 annually for three K tanks per week, including delivery and rental fees.
-
Liquid oxygen systems may require an initial setup cost exceeding $20,000, along with ongoing delivery and maintenance fees.
We are transporting the oxygen with our own car. Our [car] can hold only 6 cylinders so we should send the car to the plant every day or every other day. This problem increases the cost that we should pay for fuel and daily allowance of the purchasing staff. —Finance head
Switching to onsite oxygen generation can significantly reduce these expenses, offering long-term savings for hospitals.
Risks of Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions pose serious risks to hospitals relying on traditional oxygen delivery. Natural disasters, political instability, or logistical issues can delay shipments, leaving hospitals without critical oxygen supplies. Historical data highlights the frequency of such disruptions:
| Year Range | Number of Events | Events with Interruptions | Events with Depleted Tanks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 - 2014 | 393 | 360 | 303 |
Although we have the oxygen, sometimes we are not able to give the oxygen to patients because of a lack of gauges. —Newborn intensive care unit nurse
Onsite oxygen generation eliminates these risks by providing a continuous and reliable supply directly at the hospital.
Environmental Impact of Transporting Oxygen
Transporting oxygen using traditional methods has a significant environmental impact. The process involves multiple stages, including production, packaging, and delivery, which rely heavily on fossil fuels. Each step contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, making the system less sustainable. You can reduce these emissions by adopting onsite oxygen generation systems.
Traditional oxygen supply chains face challenges due to transportation and distribution. Long distances between production plants and hospitals increase fuel consumption. This not only raises costs but also adds to the carbon footprint. Some hospitals have reported a 30%-50% reduction in oxygen costs by minimizing transportation distances. However, last-mile distribution remains a bottleneck, further straining the environment and financial resources.
The environmental benefits of onsite oxygen generation are clear. By producing oxygen directly at the hospital, you eliminate the need for frequent deliveries. This reduces the number of vehicles on the road, cutting down on fuel usage and emissions. Additionally, onsite systems operate efficiently, ensuring a steady supply without harming the environment.
Switching to onsite oxygen generation also aligns with global efforts to combat climate change. Hospitals can play a crucial role in reducing their carbon footprint by adopting sustainable practices. This shift not only benefits the environment but also enhances the reliability of oxygen supply for patient care.
Tip: Onsite oxygen generation systems are a practical solution for hospitals looking to reduce their environmental impact while ensuring a consistent oxygen supply.
Benefits of Oxygen Generators for Hospitals
Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Savings
Oxygen generators offer significant cost savings for hospitals. Traditional oxygen procurement methods, such as bulk delivery, often involve high transportation and storage expenses. By switching to onsite oxygen generation, you can reduce costs by up to 90%. For instance, while traditional oxygen costs range from 15 per cubic meter, generated oxygen costs only
0.11. This difference translates into substantial savings over time.
| Evidence Type | Details |
|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Save 50% to 90% on purchasing costs compared to traditional methods. |
| ROI Cycle | Return on investment typically achieved within 12 to 18 months. |
| Hospital Savings | A large hospital reduced oxygen costs by 40% using onsite systems. |
Additionally, the operational model of oxygen generators ensures sustainability. Revenues from oxygen sales can cover ongoing operational costs, making the system financially viable. With proper training for biomedical engineers, you can maintain these systems efficiently, ensuring long-term functionality.
Reliability and Consistent Oxygen Supply
Reliability is critical in medical settings, where oxygen is essential for patient care. Oxygen generators provide a stable and continuous supply, eliminating the risks associated with supply chain disruptions. These systems operate with high efficiency, delivering oxygen with up to 95% purity.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Compliance | Certified with ISO 9001, ISO 13485, ISO 14001. |
| Capacity | Ranges from 2 to 189 Nm³/h. |
| Energy Consumption | As low as 1.0 kW/m³ of oxygen. |
| Stability | Ensures uninterrupted onsite oxygen supply. |
By producing oxygen onsite, you can avoid delays caused by transportation or logistical issues. This reliability ensures that hospitals can meet the oxygen demands of patients, even during emergencies or crises like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Reduced Dependency on External Suppliers
Onsite oxygen generation reduces your reliance on external suppliers. Traditional methods often depend on complex supply chains, which can be vulnerable to disruptions. With an oxygen generator, you can produce medical oxygen directly at your facility, ensuring a consistent supply.
-
The demand for oxygen generators is growing due to the increasing prevalence of respiratory diseases.
-
Home-based oxygen therapy is expanding, reducing the need for traditional oxygen cylinders.
-
Continuous onsite production supports the growing healthcare demand for oxygen.
By adopting oxygen generators, hospitals can achieve greater independence, improve operational efficiency, and enhance their ability to provide uninterrupted care to patients.
Environmental Sustainability and Reduced Carbon Footprint
Oxygen generators contribute significantly to environmental sustainability by reducing the carbon footprint of hospitals. Traditional oxygen supply methods rely on transporting cylinders over long distances, which consumes fuel and releases harmful emissions. By producing oxygen on-site, you can eliminate the need for frequent deliveries, making your hospital operations more eco-friendly.
On-site oxygen generation offers several environmental benefits:
-
It reduces carbon emissions by minimizing transportation needs.
-
Energy consumption during operation is lower compared to traditional supply chains.
-
Fuel usage and exhaust emissions from delivery vehicles are significantly decreased.
These advantages make oxygen generators a sustainable choice for hospitals aiming to reduce their environmental impact. Additionally, the advanced technology used in these systems ensures efficient energy use. For example, pressure swing adsorption (PSA) systems operate with minimal waste, further enhancing their eco-friendliness.
Switching to oxygen generators also aligns with global efforts to combat climate change. Hospitals play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and adopting sustainable practices like on-site oxygen production is a step in the right direction. By integrating these systems into your infrastructure, you not only support the environment but also ensure a reliable supply of medical oxygen for patient care.
Tip: Choosing an oxygen generator helps your hospital meet sustainability goals while maintaining high standards of medical care.
Comparing Oxygen Generators to Other Supply Methods
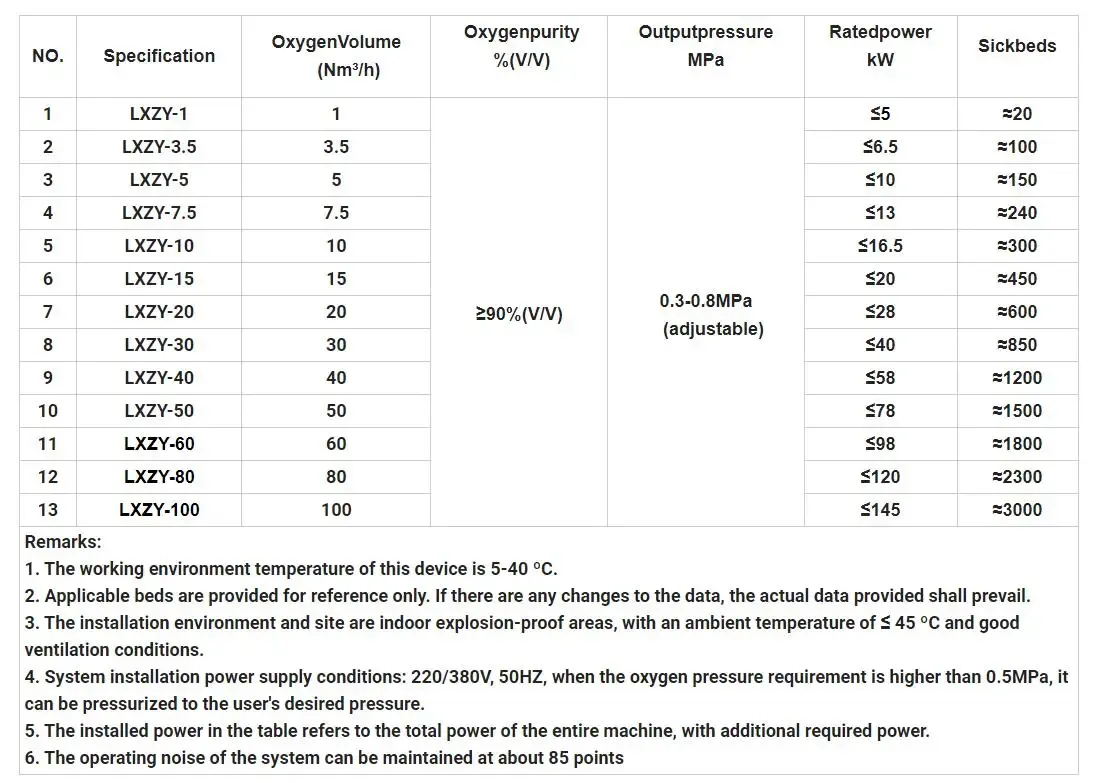
Oxygen Generators vs. Bulk Oxygen Delivery
When comparing oxygen generators to bulk oxygen delivery, you’ll notice significant differences in cost, efficiency, and infrastructure needs. Bulk oxygen delivery involves transporting liquid or compressed oxygen to hospitals, which requires storage tanks and regular refills. This method works well for facilities with high oxygen demands but comes with logistical challenges.
Oxygen generators, on the other hand, produce oxygen onsite using advanced technology like pressure swing adsorption (PSA). They eliminate the need for transportation and storage, reducing costs over time. While bulk delivery provides highly purified oxygen, generators offer a steady supply with up to 95% purity, suitable for most medical applications. Hospitals using generators can avoid supply chain disruptions and ensure consistent oxygen availability.
| Oxygen Supply Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| PSA Oxygen Generators | High volume, onsite production, cost-effective | Significant upfront investment |
| Bulk Oxygen Delivery | Ideal for high-demand settings, highly purified | Requires storage and distribution infrastructure |
Oxygen Generators vs. Oxygen Concentrators
Oxygen generators and portable oxygen concentrators serve different purposes in healthcare. Concentrators are compact devices designed for individual use, often in home settings. They extract oxygen from ambient air using PSA technology, making them ideal for patients needing continuous oxygen therapy. However, they have limited capacity and are unsuitable for critical care or high-demand scenarios.
Oxygen generators, in contrast, produce larger volumes of oxygen, making them suitable for hospitals and industrial applications. They can supply multiple patients simultaneously and integrate directly into medical pipeline systems. Generators excel in performance and reliability, especially in high-demand situations.
-
Oxygen Concentrators: Portable, compact, and suitable for home use. Best for non-critical patients.
-
Oxygen Generators: High-volume production, ideal for healthcare facilities. Reliable for critical care.
Pros and Cons of Each Method
Each oxygen supply method has unique advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these can help you choose the best option for your facility.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk Oxygen Supply | Stable supply, suitable for large facilities | High initial costs, requires transportation |
| Portable Oxygen Concentrator | Compact, portable, ideal for home use | Limited capacity, shorter lifespan |
| Medical Oxygen Generators | Cost-efficient, reliable, reduced dependency | High upfront investment, maintenance required |
Oxygen generators stand out for their cost-effectiveness and reliability in medical settings. They reduce dependency on external suppliers and ensure a consistent oxygen supply, making them a practical choice for hospitals.
Real-World Examples of Hospitals Using Oxygen Generators
Case Study 1: A Regional Hospital in California
A regional hospital in California faced challenges in maintaining a steady oxygen supply during emergencies. The management decided to install an onsite oxygen generator to address these issues. This system allowed the hospital to produce oxygen directly on its premises, eliminating the need for frequent deliveries. As a result, the hospital reduced its oxygen costs by 40%.
The onsite generator also enhanced the hospital's emergency response capabilities. During a recent wildfire crisis, the hospital maintained a stable oxygen supply despite disruptions in transportation networks. This reliability ensured that patients received uninterrupted care, even under challenging circumstances.
| Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Onsite oxygen generators reduce dependency on external suppliers, leading to long-term cost-effectiveness despite higher initial costs. |
| Emergency Response | Hospitals using onsite generators have improved their emergency response capabilities by ensuring a stable oxygen supply. |
Case Study 2: A Multi-Specialty Hospital in India
A multi-specialty hospital in India implemented an oxygen generator to meet the growing demand for medical oxygen. Before this, the hospital relied on external suppliers, which often led to delays and increased costs. The new system provided a continuous oxygen supply, significantly improving operational efficiency.
The hospital also reported better compliance with health regulations due to the autonomous nature of the generator. This system ensured that oxygen purity levels consistently met medical standards. By reducing dependency on third-party suppliers, the hospital saved on transportation costs and improved patient outcomes.
-
A large hospital reported a 40% reduction in oxygen costs after installing onsite oxygen systems.
-
The autonomous oxygen delivery system enhances safety and compliance with health regulations.
Lessons Learned and Success Stories
These case studies highlight the transformative impact of oxygen generators in healthcare settings. Hospitals that adopt these systems experience significant cost savings and operational improvements. Onsite oxygen generation ensures a stable supply, even during emergencies, reducing the risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
You can also achieve environmental benefits by minimizing transportation needs. This shift aligns with global sustainability goals while ensuring that patients receive the care they need. By investing in oxygen generators, hospitals can enhance their ability to provide reliable and efficient care, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Oxygen generators solve critical challenges in hospital oxygen supply by offering a reliable and sustainable solution. They ensure a stable flow of medical oxygen, reducing reliance on external suppliers. This reliability enhances patient care, especially during emergencies. On-site production also minimizes transportation barriers, making oxygen more accessible and cost-effective for hospitals.
-
On-site systems reduce gas leakage and environmental pollution.
-
They lower operational costs and improve resource efficiency.
-
PSA oxygen generators provide continuous medical oxygen production, ensuring consistent supply for patients.
By adopting oxygen generators, hospitals can achieve long-term savings, improve care quality, and align with green practices.
FAQ
What is the lifespan of an oxygen generator?
Most oxygen generators last 10 to 15 years with proper maintenance. Regular servicing and timely replacement of parts ensure optimal performance. You should follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance schedules.
How much energy does an oxygen generator consume?
Energy consumption depends on the model and capacity. On average, a generator uses 1.0 kW per cubic meter of oxygen produced. You can reduce energy costs by choosing energy-efficient models.
Tip: Check the energy efficiency rating before purchasing a generator to save on operational costs.
Can oxygen generators handle emergency situations?
Yes, oxygen generators provide a continuous supply of oxygen, even during emergencies. They eliminate delays caused by transportation or supply chain disruptions. Hospitals can rely on them for uninterrupted oxygen availability.
Are oxygen generators environmentally friendly?
Oxygen generators are eco-friendly. They reduce carbon emissions by eliminating the need for transportation. Advanced systems like PSA technology also minimize energy waste, making them a sustainable choice for hospitals.
Do oxygen generators require a lot of maintenance?
Maintenance is straightforward and involves regular checks of filters, compressors, and molecular sieves. Following the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule ensures reliability and extends the generator’s lifespan.
Note: Proper training for staff can simplify maintenance and reduce downtime.